On this page
Subscribe for updates
Keep up with OrderEase and access industry-leading order operation insights.
In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency and seamless data flow are more important than ever. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become essential tools for businesses of all sizes, helping them manage everything from finances to supply chains and customer relations. However, an ERP system alone isn’t enough. To unlock its full potential, it needs to be integrated with other software and systems across the business. This is where ERP integration comes in.
An ERP integration involves connecting your organization’s system with other business applications like EDI and eCommerce channels. This data sharing enhances operational efficiency, improves decision-making, and provides a holistic view of business processes. The benefit of ERP integration is aligning departments with each other, streamlining operational workflows, and driving new productivity and growth.
What is ERP Integration in Business?
ERP integration connects your ERP to external order channels and partner systems via EDI/APIs/portals and to internal apps (eCommerce, POS, shipping/WMS).
The goal is a unified, near-real-time order flow and a single source of truth in the ERP, not direct ERP-to-ERP coupling across companies.
In a B2B (business-to-business) context, ERP integration enables seamless communication and data exchange between a company's ERP system and those of its suppliers, customers, and partners, enhancing collaboration, automating workflows, and providing real-time insights for better decision-making across the business ecosystem.
How Does ERP Integration Work?
ERP integration links your ERP with every system that powers your B2B workflow, from eCommerce and EDI channels to shipping, POS, and inventory tools. Traditional setups rely on middleware or custom builds to bridge incompatible systems.
OrderEase replaces that patchwork with a “connect-once” model: integrate your ERP once, and OrderEase syncs every order, invoice, inventory update, and acknowledgment across all channels in real-time or near real-time.
- EDI: Automates structured B2B document exchange (POs, invoices, ASNs) with retailers and suppliers.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces):
APIs allow different software systems to communicate and share data in real time with eCommerce, marketplaces, and shipping tools. Many modern ERP systems offer built-in APIs that make it easier to connect with other software. - Pre-built Connectors: Remove the need for heavy middleware by plugging directly into major ERPs (NetSuite, Sage, QuickBooks, Acumatica) and retail networks.
- Custom Integrations:
In some cases, businesses may need custom integrations to connect their ERP system with unique or legacy software. This typically involves working with developers to build tailored solutions.
With OrderEase, ERP integration stops being a coding exercise and becomes a scalable backbone, one connection that standardizes every B2B order flow from intake to fulfillment.
When Should My Business Add Integrations to Its ERP System?
In the past, many businesses have overlooked integration due to the high cost and difficulty of implementation. Online commerce was predominantly geared toward consumer goods and online solutions mainly supported the B2C marketplace. The B2B world, always around 10-15 years behind B2C, was perfectly happy with emailing and faxing their orders in the old-fashioned way.
However, many of those same consumers are also business owners who’ve quickly become used to the convenience of B2C ordering and want the same for their B2B relationships, and this demand isn’t going unnoticed. Many large companies are quickly adopting fully automated integrations for all their systems. ERP integration is no longer a case of “Should I, or shouldn’t I?” It’s a question of “Can I afford to put off integrations any longer?"
To make matters more pressing, the widespread adoption of mobile devices in the wholesale ecosystem has driven suppliers to provide their customers with an anytime, anywhere integrated ordering solution. Not only that, they’re restructuring their websites and online ordering solutions to be more responsive to the mobile marketplace.
Is B2B ERP Integration Worth It for Small Businesses?
For smaller wholesalers, distributors, and manufacturers, connecting your ERP or even accounting software like Sage or QuickBooks to your order channels creates huge efficiency gains. With a connect-once setup like OrderEase, small teams can sync every order, invoice, and inventory update automatically across eCommerce, EDI, and partner systems.
Here’s why it’s worth it for small businesses:
- Automate order capture from email, EDI, and portals, no more manual re-keying.
- Reduce admin labor and costly fulfillment mistakes.
- Maintain alignment among suppliers, distributors, and customers through real-time data sharing.
- Grow into new channels without technical rebuilds.
- Deliver faster service and better accuracy with the same lean team.
These advantages mirror the broader benefits of ERP integration we discussed earlier, but are especially impactful for smaller teams with leaner resources.
Why is ERP Integration Important?
- Improved Efficiency:
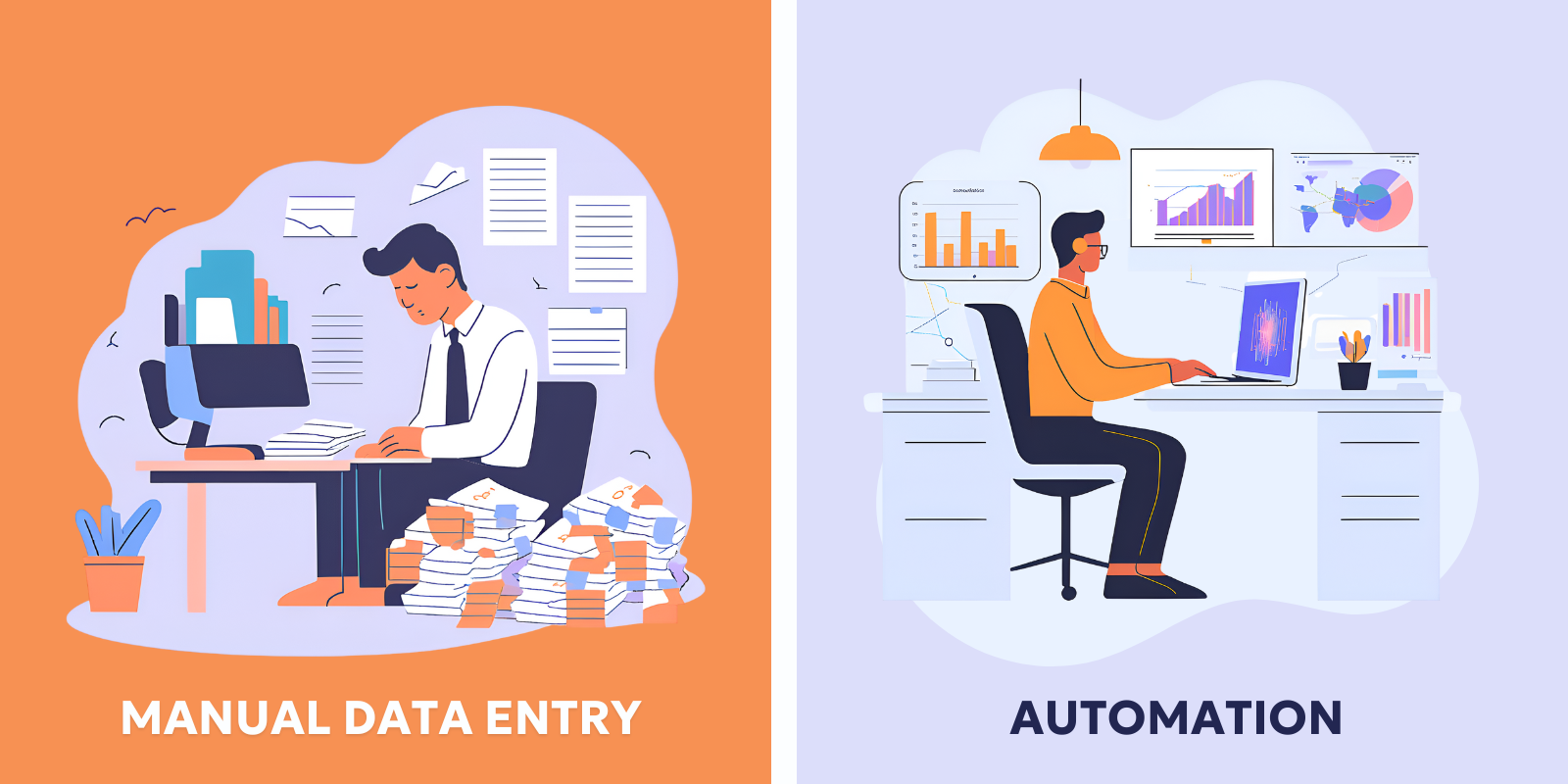
Without ERP integration, employees may need to manually enter the same data into multiple systems. This repetitive task takes time, increases the risk of errors, and ultimately slows down business processes. ERP integration automates data flow across various systems, making it easier to access and share important information quickly, thereby improving operational efficiency. - Real-Time Data Sharing:
One of the key benefits of ERP integration is the ability to share data in real time. This means that information about inventory, sales, or customer interactions is updated across all systems instantly. For instance, if a customer places an order through an e-commerce platform, the ERP can automatically update inventory levels and trigger the shipping process. This leads to faster decision-making, more accurate reporting, and a smoother overall customer experience. - Better Decision Making:
With integrated data, businesses have a clearer, more accurate view of their operations. Real-time access to information across all departments—from finance to sales to supply chain—enables better forecasting, budgeting, and performance tracking. Business leaders can make more informed decisions, spot inefficiencies, and identify opportunities for growth. - Reduced Costs and Errors:
Manual data entry between systems can lead to costly mistakes, such as incorrect orders, missed shipments, or discrepancies in financial records. ERP integration helps minimize these risks by eliminating the need for manual intervention. This not only reduces errors but also helps lower costs related to rectifying mistakes, including customer dissatisfaction and lost sales. - Scalability and Flexibility:
As businesses grow, so do their software needs. ERP integration makes it easier to scale your operations and connect new tools and platforms as your business evolves. Whether you're adding new departments, entering new markets, or integrating new software, an integrated ERP system ensures that your processes remain connected and efficient.
What Are the Risks of ERP System Integration?
Most businesses purchase and deploy an ERP system long before they even start to consider an online ordering solution to allow their customers to place orders and make payments via the internet. Usually, when a purchase decision is made to build out online ordering, it’s typically kept separate from the ERP for change management reasons.
If your ERP and online ordering solution have their own databases, any changes implemented in one system have to be transferred to another, requiring manual data entry.
Waiting for a database update before you can process orders, replenish inventory levels, or update availability for your customers will result in slower operations and a higher risk of database errors.
Depending on your integration provider, you’ll likely face four issues in ERP implementation:
- High Initial Costs:
Custom-built ERP integrations can quickly ramp up in price. This is especially true for order management if you need to connect to multiple retail partners or eCommerce sites. - Complex Implementation:
Implementing change projects on your ERP can be risky, and implementation for specific business needs can take months longer than you’d normally expect. Implementations also usually require long-term maintenance. - Resistance to Change:
ERP implementations can fundamentally change how employees work in their day-to-day activities. There is a high risk of change management failure for any major change in workflow through ERPs. Employees must be brought on board with an ERP implementation for it to work.
What Are the Different Types of ERP Integration?
You can break ERP integrations into two main groups: one-way and two-way.
- One-way Integrations:
Data tables get pushed to online ordering solutions through an established API framework, typically manually or automatically at scheduled intervals. In this ERP integration method, information only flows one way. - Two-way Integrations:
Also known as fully automated integrations, two-way integrations synchronize the data between systems, keeping everything up to date in real-time. Data is updated and passed back and forth between your ERP and your online ordering systems.
When Evaluating a Solution for ERP Integration
When evaluating a solution to integrate your ERP with other systems to make order management more efficient—shipping software, sales channels, online marketplaces, order management, and mobile ordering solutions—you need to be aware of the different options that exist for how an integration communicates with the other side.
There are three main communication standards integrations can work with:
- EDI: The main standard for large retailers.
- API: The standard for many eCommerce sites.
- sFTP: A more secure, but slower method of transferring data.
With each of these, there may be limitations on what information can be transmitted due to limitations of functionality. However, the most important thing organizations should take into consideration is the underlying functionality of their integrations.
ERP Integration Trends
As with most B2B trends, everyone has been 10-20 years behind on the zeitgeist of B2C buying habits. Your customers, long accustomed to the ease of ordering from major commercial companies such as Amazon, want the same ease in their B2B orders.
To meet consumer demand, businesses are implementing ERP system integration to simplify online orders and how your customers can interact with your products.
- Mobile Orders:
ERP mobile ordering has become a hot new trend in the wholesale world. Your customers want to be able to order on the go, from wherever. Your salespeople out in the field want to be able to do the same. With a mobile ordering system connected directly to your ERP, your customers and reps will be able to order right from the floor or warehouse, giving them a more tactile connection. - Web Order Integrations:
Integrations of your ERP with your eCommerce ventures can not only vastly improve your customer service but also deliver a more personalized customer experience. With self-service features and a wide variety of catalog options, an ERP integration for web orders can significantly change how you sell on the web by easing the diversification of sales channels and providing the opportunity for self-service orders. - ERP Integrations to Marketplaces:
Having an ERP marketplace integration (or integrations) is vital to the long-term viability of marketplaces for your business. An ERP marketplace integration automates the majority of the tasks that would otherwise be laborious, including data transfer and the bulk of your order management tasks.
Choosing the Right Communication Method for ERP Integration
When integrating your ERP with systems like shipping software, online marketplaces, or mobile ordering tools, it’s not just about whether the systems connect but how they communicate. The method determines how fast, reliable, and automated your data flow will be.
Here are the most common communication methods used in ERP integrations and when to consider each:
|
Method |
When to Use It |
How It Works |
|
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) |
Best for companies that exchange a lot of documents with retailers or suppliers, such as purchase orders or invoices. |
EDI is a common system used by large retailers and distributors. It replaces paper and email documents with structured digital files, letting businesses trade data automatically. |
|
Application Programming Interface (API) |
Great for modern tools that need instant updates, like eCommerce stores, mobile apps, or delivery platforms. |
An API works like a live conversation between systems. When an order is placed or stock levels change, both systems know right away. |
|
Secure File Transfer Protocol (sFTP) |
Useful for older or traditional systems that still rely on file uploads |
sFTP moves data between systems in encrypted files, keeping it private and safe. Businesses often use it for scheduled updates, like sending a daily file of new orders or stock numbers overnight. It’s slower than real-time connections but works well when speed isn’t critical. |
With each of these, there may be limitations on what information can be transmitted due to limitations of functionality. However, the most important thing organizations should take into consideration is the underlying functionality of their integrations.
The Tools You Can Use for ERP Integration
Integrating your ERP system with other business applications is key to streamlining operations and ensuring accurate, real-time data flow across your organization. There are several tools and platforms available that can simplify the process of ERP integration, depending on your business needs and system requirements. Here’s a look at some of the most effective tools you can use for ERP integration:
- Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS):
iPaaS solutions are cloud-based platforms designed to integrate various business applications, data, and systems. They are often marketed as quick, user-friendly solutions for ERP integrations, and many offer pre-built connectors to various third-party applications. - Middleware Solutions:
Middleware is a software layer that connects different applications, enabling them to communicate with each other. It serves as a bridge between your ERP system and other business tools, allowing data to flow seamlessly between them. - OrderEase:
As a B2B Order Management System, is designed to centralize and automate the order intake process from every channel (eCommerce, field reps, EDI, email) and connect seamlessly with your ERP. OrderEase improves visibility, reduces manual work, and delivers a modern, self-service experience for both internal teams and customers.
.png?width=1600&height=800&name=Blog%20Imagery%20(10).png)
Connecting Your ERP
ERP integrations are an essential step for businesses looking to improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and streamline operations. By connecting your ERP system with other business tools and platforms—whether through APIs, middleware, or custom integrations—you can reduce errors, lower costs, and scale your business for growth. However, it’s important to consider the costs, complexity, and impact of implementing an ERP integration solution to ensure it aligns with your business needs and goals.
If you're ready to integrate your ERP, get in touch with the OrderEase team!
FAQs
ERP Ordering System vs Integrated Software: What’s the Key Difference?
An ERP ordering system focuses specifically on managing orders within your ERP system, tracking sales, inventory, and customer data. In contrast, integrated software combines multiple business functions such as accounting, HR, and supply chain management into one unified platform. The key difference is that an integrated system connects various business processes, whereas an ERP ordering system is more specialized for order management.
How Long Does a Typical ERP Integration Solution Take?
The time it takes to implement an ERP integration solution can vary depending on factors like the complexity of the system, the number of applications being integrated, and the scale of your business. On average, an intégration ERP project can take anywhere from a few months to a year. It's important to work with experienced professionals who can provide a realistic timeline based on your specific needs.
What are Some Essential Insights Before Starting Your ERP Integration B2B Project?
Before starting an ERP integration B2B project, it's crucial to understand the scope of integration, the systems you plan to connect, and the business goals you're aiming to achieve. Proper planning and clear communication with your business partners will help ensure smooth integration. Consider factors like data security, user training, and ongoing support to maximize the success of your b2b erp integration.
What are the Best Tools and Platforms for ERP Marketplace Integration?
For ERP marketplace integration, several tools and platforms are popular for their ease of use and powerful features. Look into platforms like SAP, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 for comprehensive ERP integration solutions. These tools offer flexibility, scalability, and a wide range of integrations with marketplaces, ensuring that your ERP system can efficiently sync with external platforms for smooth transactions.
.png?width=80&height=80&name=Amazon%20Logo%20(2).png)
Subscribe for updates
Keep up with OrderEase and access industry-leading order operation insights.
Lorem ipsum title
lorem ipsum dolor sit ammet lorem ipsum dolor sit ammet lorem ipsum dolor sit ammet lorem ipsum dolor sit ammet.
.png?height=290&name=What%20is%20ERP%20Integration%20(5).png)
